Written by Craig
May 24, 2023
Problems, not solutions, create spaces for innovation. ~Ash Maurya
Identifying problems is a key aspect of successful innovation. As startup founders, it’s important to understand that the real opportunity for innovation lies not in the solutions, but in the problems that need to be solved. By honing in on the issues faced by your target audience, you can tap into untapped market potential and create a product or service that truly resonates with their needs.
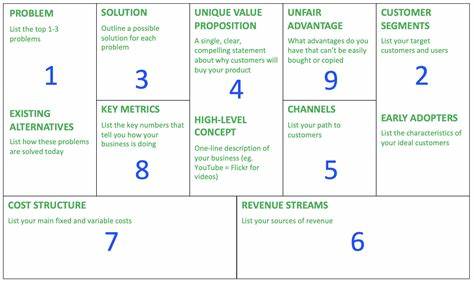
One effective way of identifying problems is through the use of a Lean Canvas, and in particular the four specific boxes of the Leaner Canvas. The Lean Canvas is a tool that allows you to organize and prioritize the various elements of your business model. When filling out the Lean Canvas, it’s critical to pay close attention to the “Problems” box. This is where you can identify the challenges faced by your target audience with existing solutions.
Focus on the top 1-3 problems
It is tempting to focus on your solution, at the end of the day, that is what you are good at and that is the essence of your idea as a founder. However, the most important thing to remember is: Investors don’s care about your solution, aka product or service, they care about traction (customer engagement). Customers don’t care about your solution either, they care about their problems and how your product solves them (Unique Value Proposition) better than the competition.
With this in mind, your initial objective when starting a company is NOT focusing on and building a solution but designing your entire business model.
Your Business Model is the product, not your solution.
When designing your business model, your goal is to find a big problem that a large market segment NEEDS a solution for. You can begin by identifying a market you want to go after and identifying the jobs this market needs done. For example, everyone needs to wash the dishes. You can then focus on the The “Existing Alternatives” box on the Lean Canvas is an essential tool for identifying problems.
When completing this section, it’s important to consider a range of alternatives, such as competitors, substitutes, and complementary products. For example, a sink of soapy water, existing dishwashers, or throw away paper plates.
This will give you a more comprehensive understanding of the ways your target audience accomplishes the job now and highlight potential opportunities for innovation.
Identifying problems is a fundamental step in the innovation process. By utilizing the Lean Canvas to focus on customer, market, and company jobs to be done, considering what existing alternatives there are to accomplishing these jobs, and what the problems are with these existing alternatives, you can identify opportunities for innovation and create a product or service that truly resonates with your target audience.
As demonstrated by Bosch, identifying problems and taking advantage of untapped market potential can lead to major success. Bosch identified the need for quiet dishwashers that could operate quietly enough to not interrupt people in the family room adjacent to the kitchen. They then created a revolutionary quiet dishwasher that has seen tremendous market success.
By focusing on your entire business model, solving a problem for a big market, you can craft a business that is setup for success without writing a line of code or designing a prototype. Love the problem.
Here are top tips on how to use a Lean canvas to find a BIG problem:
Identify your customer segment:
Identify a specific group of customers that you are familiar with. The more familiar you are with them, the better. Being familiar will play well when you provide your “Why?” to investors because you understand the space.
What are they trying to accomplish?
Identify an important objective of this customer segment. What is the job to be done?
What are the existing alternatives?
How do they reach their goal today? Not just directly competing tech, but also low tech alternatives.
Identify the problems with the existing alternatives:
What is the problem with the existing alternatives that is making your target market want to switch? This should be a problem that your target customers are facing, and it should be specific and well-defined.
Develop a unique value proposition:
This is where you explain how your business solves the problem in a unique way that sets it apart from competitors. Your unique value proposition should be simple, concise, and easy to understand.
Outline your solutions:
Detail the specific products or services that your business will offer to solve the customer’s problem. Be specific and make sure that these solutions directly address the problem you have identified.
Determine your channels:
Think about how you will reach your customers and deliver your solutions to them. This could involve online channels, in-person channels, or a combination of both.
Determine your revenue streams:
Identify the ways your business will generate revenue. This could include sales, subscriptions, advertising, or other methods.
Identify your cost structure:
List the key costs associated with running your business, such as product development, marketing, and operations. Be as specific as possible, and include both fixed and variable costs.
Identify key metrics:
Choose the metrics that will be used to track the success of your business. These could include customer acquisition, retention, revenue, or other metrics that are specific to your business.
Highlight your unfair advantage:
This is where you explain what makes your business unique and difficult for competitors to copy. This could include a patented technology, a large, loyal customer base, or other advantages that are specific to your business.
Remember, the Lean Canvas is a flexible tool, and you may need to iterate and adjust your answers as you learn more about your customers and market. The goal is to use the Lean Canvas to create a simple, concise, and effective communication of your business model that can be used to test and validate your ideas.
Related Articles

Marketing messages that resonate
By understanding your customers and their needs, you can create a marketing message that really resonates with them The Jobs to be Done theory is a powerful framework for understanding consumer behavior and the driving forces behind innovation. This theory, developed...
Don’t write a traditional business plan
A business model describes how you create, deliver, and capture value (get paid) from customers. ~Saul Kaplan Deconstructing an idea for a product or business is a crucial step in the development process. By breaking down the concept into its core components, you can...

Don’t write a traditional business plan
A business model describes how you create, deliver, and capture value (get paid) from customers. ~Saul Kaplan Deconstructing an idea for a product or business is a crucial step in the development process. By breaking down the concept into its core components, you can...
Stay Up to Date With The Latest News & Updates
Access Premium Content
Join Our Newsletter
Follow Us

0 Comments